| | |
GAUDI User Guide

In this chapter we give an overview of the various services, other than the data access services, which are available for use within the Gaudi framework. The Job Options service, the Message service and the Particle Properties service are available in this release.
We also describe how to implement new services for use within the Gaudi environment. We look at how to code up a service, what facilities the Service base class provides and how a service is managed by the application manager.
The Job Options Service is a mechanism which allows to configure an application at run time, without the need to recompile or relink. The options, or properties, are set via a job options file, which is read in when the Job Options Service is initialised. In what follows we describe the new format of the job options file, including some examples. Please note that this syntax is different to that used in previous releases of the Gaudi software.
The job options file has a well-defined syntax (similar to a simplified C++-Syntax) without datatypes. The datatypes are recognised by the "Job Options Compiler", which interprets the job options file according to the syntax (described in Appendix Appendix C together with possible compiler error codes).
The job options file is an ASCII-File, composed logically of a series of statements. The end of a statement is signaled by a semicolon (';') - as in C++.
Comments are the same as in C++, with '//' until the end of the line, or between '/*' and '*/'.
There are three constructs which can be used in a job options file:
An assignment statement assigns a certain value (or a vector of values) to a property of an object or identifier. An assignment statement has the following structure:
<Object / Identifier> . < Propertyname > = < value >; |
The first token (Object / Identifier) specifies the name of the object whose property is to be set. This must be followed by a dot ('.')
The next token (Propertyname) is the name of the option to be set, as declared in the declareProperty() method of the IProperty interface. This must be followed by an assign symbol ('=').
The final token (value) is the value to be assigned to the property. It can be a vector of values, in which case the values are enclosed in array brackets ('{`,'}`), and separated by commas (,). The token must be terminated by a semicolon (';').
The type of the value(s) must match that of the variable whose value is to be set, as declared in declareProperty(). The following types are recognised:
Please note that it is not necessary any more to define in the job options file the type for the value which is used. The job options compiler will recognize by itself the type of the value and will handle this type correctly.
Because of the possibility of including other job option files (see below), it is sometimes necessary to extend a vector of values already defined in the other job option file. This functionality is provided be the append statement.
An append statement has the following syntax:
<Object / Identifier> . < Propertyname > += < value >; |
The only difference from the assignment statement is that the append statement requires the '+=' symbol instead of the `=' symbol to separate the Propertyname and value tokens.
The value must be an array of one or more values
The job options compiler itself tests if the object or identifier already exists (i.e. has already been defined in an included file) and the type of the existing property. If the type is compatible and the object exists the compiler appends the value to the existing property.
It is possible to include other job option files in order to use pre-defined options for certain objects. This is done using the #include directive:
#include "filename.ext" |
The "filename.ext" can also contain the path where this file is located. The include directive can be placed anywhere in the job option file, but it is strongly recommended to place it at the very top of the file (as in C++).
As mentioned above, you can append values to vectors defined in an included job option file. The interpreter creates these vectors at the moment he interprets the included file, so you can only append elements defined in a file included before the append-statement!
As in C/C++, an included job option file can include other job option files. The compiler checks itself whether the include file is already included or not, so there is no need for #ifndef statements as in C or C++ (and they are in any case not supported!).
Sometimes it is necessary to over-ride a value defined previously (maybe in an include file). This is done by using an assign statement with the same object and propertyname. The last value assigned is the valid value!
We have already seen an example of a job options file in Listing 2 in Chapter 4 . That example was the job options file distributed with the GaudiExamples/Histograms example application. Note the inclusion of a system dependent standard job file. These are shown in Listing 29 and Listing 30 for WNT and Unix respectively, and are intended to set up a set of default options common to all of the distributed examples.
Listing 29 The Standard Include Job Option File for NT Systems
Listing 30 The Standard Include Job Option File for UNIX Systems
One of the components directly visible to an algorithm object is the message service. The purpose of this service is to provide facilities for the logging of information, warnings, errors etc. The advantage of introducing such a component, as opposed to using the standard std::cout and std::cerr streams available in C++ is that we have more control over what is printed and where it is printed. These considerations are particularly important in an online environment.
The Message Service is configurable via the job options file to only output messages if their "activation level" is equal to or above a given "output level". The output level can be configured with a global default for the whole application:
|
// Set output level threshold (2=DEBUG, 3=INFO, 4=WARNING, 5=ERROR, 6=FATAL) |
and/or locally for a given client object (e.g. myAlgorithm):
Any object wishing to print some output should (must) use the message service. A pointer to the IMessageSvc interface of the message service is available to an algorithm via the accessor method messageService(), see section 5.2 . It is of course possible to use this interface directly, but a utility class called MsgStream is provided which should be used instead.
The
MsgStream
class is responsible for constructing a Message object which it then passes onto the message service. Where the message is ultimately sent to is decided by the message service.
In order to avoid formatting messages which will not be sent because the verboseness level is too high, a MsgStream object first checks to see that a message will be printed before actually constructing it. However the threshold for a MsgStream object is not dynamic, i.e. it is set at creation time and remains the same. Thus in order to keep synchronized with the message service, which in principle could change its printout level at any time, MsgStream objects should be made locally on the stack when needed. For example, if you look at the listing of the HistoAlgorithm class (see also Listing 31 below) you will note that MsgStream objects are instantiated locally (i.e. not using new) in all three of the IAlgorithm methods and thus are destructed when the methods return. If this is not done messages may be lost, or too many messages may be printed.
The MsgStream class has been designed to resemble closely a normal stream class such as std::cout, and in fact internally uses an
ostrstream
object. All of the MsgStream member functions write unformatted data; formatted output is handled by the insertion operators.
An example use of the MsgStream class is shown below.
When using the MsgStream class just think of it as a configurable output stream whose activation is actually controlled by the first word (message level) and which actually prints only when "endreq" is supplied. For all other functionality simply refer to the C++
ostream
class.
The "activation level" of the MsgStream object is controlled by the first expression, e.g. MSG::ERROR or MSG::DEBUG in the example above. Possible values are given by the enumeration below:
enum MSG::Level { VERBOUS, DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, FATAL }; |
Thus the code in Listing 31 will produce NO output if the print level of the message service is set higher than MSG::ERROR. In addition if the service's print level is lower than or equal to MSG::DEBUG the "Finalize completed successfully" message will be printed (assuming of course it was successful).
What follows is a technical description of the part of the MsgStream user interface most often seen by application developers. Please refer to the header file for the complete interface.
The MsgStream class overloads the '<<` operator as described below.
The MsgStream specific manipulators are presented below, e.g. endreq: MsgStream& endreq(MsgStream& stream). Besides these, the common
ostream
and ios manipulators such as std::ends, std::endl,... are also accepted.
The Particle Property service is a utility to find information about a named particle's Geant3 ID, Jetset/Pythia ID, Geant3 tracking type, charge, mass or lifetime. The database used by the service can be changed, but by default is the same as that used by SICb.
This service is created by default by the application manager, with the name "ParticlePropertySvc."
In order to use the service, a client must access its interface,
IParticlePropertySvc
. From an algorithm this is done as follows:
The Particle Property Service currently only has one property:
ParticlePropertiesFile
. This string property is the name of the database file that should be used by the service to build up its list of particle properties. The default value of this property, on all platforms, is
$LHCBDBASE/cdf/particle.cdf
As mentioned earlier, the service implements the
IParticlePropertySvc
interface which must be included when a client wishes to use the service - the file to include is
Gaudi/Interfaces/IParticlePropertySvc.h
The service itself consists of one STL vector to access all of the existing particle properties, and three STL maps, one to map particles by name, one to map particles by Geant3 ID and one to map particles by stdHep ID.
Although there are three maps, there is only one copy of each particle property and thus each property must have a unique particle name and a unique Geant3 ID. The third map does not contain all particles contained in the other two maps; this is because there are particles known to Geant but not to stdHep, such as Deuteron or Cerenkov. Although retrieving particles by name should be sufficient, the second and third maps are there because most of the data generated by SICb stores a particle's Geant3 ID or stdHep ID, and not the particle's name. These maps speed up searches using the IDs.
The IParticlePropertySvc interface provides the following functions:
The IParticlePropertySvc interface also provides some typedefs for easier coding:
Below are some extracts of code from the example in GaudiExamples/ParticleProperties, to show how one might use the service:
Within Gaudi we use the term "Service" to refer to a class whose job is to provide a set of facilities or utilities to be used by other components. In fact we mean more than this because a concrete service must derive from the Service base class and thus has a certain amount of predefined behaviour; for example it has intialize() and finalize() methods which are invoked by the application manager at well defined times.
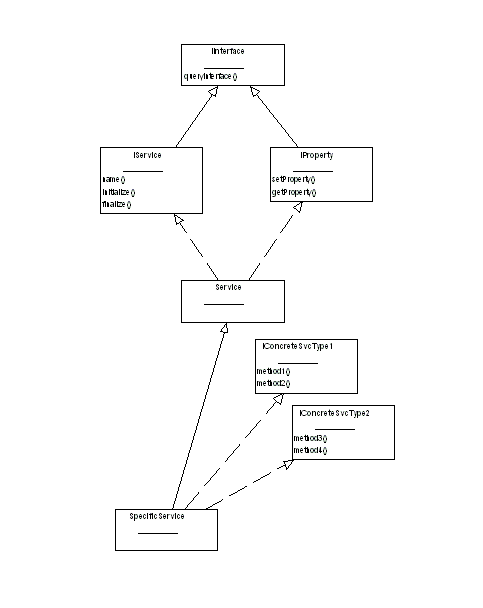
|
Figure 15 shows the inheritance structure for an example service called SpecificService (!). The key idea is that a service should derive from the Service base class and additionally implement one or more pure abstract classes (interfaces) such as IConcreteSvcType1 and IConcreteSvcType2 in the figure.
As discussed above, it is necessary to derive from the Service base class so that the concrete service may be made accessible to other Gaudi components. The actual facilities provided by the service are available via the interfaces that it provides. For example the ParticleProperties service implements an interface which provides methods for retrieving, for example, the mass of a given particle. In figure 15 the service implements two interfaces each of two methods.
A component which wishes to make use of a service makes a request to the application manager. Services are requested by a combination of name, and interface type, i.e. an algorithm would request specifically either IConcreteSvcType1 or IConcreteSvcType2.
The identification of what interface types are implemented by a particular class is done via the queryInterface method of the IInterface interface. This method must be implemented in the concrete service class. In addition the initialize() and finalize() methods should be implemented. After initialization the service should be in a state where it may be used by other components.
The service base class offers a number of facilities itself which may be used by derived concrete service classes:
The following is essentially a checklist of the minimal code required for a service.